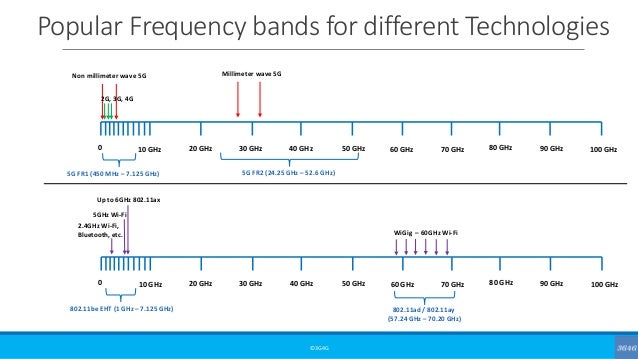
Then theres high-band 5G which uses millimeter-wave bands in the range of 2539 GHz. Varying 100 µs min to 4ms max Latency.
 Beginners 5g Spectrum Short Version
Beginners 5g Spectrum Short Version
Its real-world speeds range from 50 Mbps to 3 Gbps.
4g vs 5g frequency. Thats a big contrast from the high-frequency 5G networks which offer speeds 100 times greater than 4G. TTI Transmission Time Interval 1 ms. Carrier Bandwidth 14 MHz to 20 MHz 45G-Extension of 4G LTE.
The aim with 5G is to hit 50Mbps as an average minimum however right now the minimum is quite a bit lower and the average sits around 57Mbps according to. 10 Mbps to 150 Mbps as per standard release Peak Data rate for Uplink. A frequency of 600 MHz for example has lower bandwidth but because its not affected as easily by things like moisture in the air it doesnt lose power as quickly and is able to reach 5G phones and other 5G devices further away as well as better penetrate walls to provide indoor reception.
Both lower and higher frequency 5G should eventually reach most of the region giving us the best of both worlds. 4G was a great leap forward allowing people to stream music and video on the go. Theoretically 5G could be 100 times faster than 4G with the maximum speeds of around 20 Gbps.
Eventually 5G will also be launched on higher frequencies of between 30GHz and 300GHz known as millimetre wave or mmWave. The range goes to an upper limit of up to 300 GHz. 5G network uses unique radio frequencies to bring the output that 4G networks fail to bring.
800MHz Band 20 900MHz Band 8 1400MHz SDL Band 32. Speed is the most commonly used factor when comparing 5G vs 4G. Eventually both lower and higher frequency 5G will cover much of.
Cat4 Cat1 Peak Data rate for Downlink. The second frequency band creates a major difference between 5G and 4G. 5G NR can include lower frequencies FR1 below 6 GHz and higher frequencies FR2 above 24 GHz.
One underlying difference is 5Gs use of unique radio frequencies to achieve what 4G networks cannot. Currently 5G is offered on the same mid-range radio frequencies as 3G and 4G below 6 Gigahertz or GHz and network providers plan to re-purpose old and out-of-use 2G spectrum to further expand 5G coverage. It is a high-frequency band with millimeter-wave mmWave and frequencies above 24 GHz.
10 ms radio. 5 Mbps to 50 Mbps as per standard release Used frequency BW. Massive Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output MIMO 64-256 antennas offer performance speeds that are ten times better than the current 4G networks.
4G LTE The primary technologies behind 5G include 26 28 38 60GHz millimeter wave bands. 4G uses frequencies below 6 GHz while some 5G networks use higher frequencies like around 30 GHz or more. 2Mbps to 1Gbps.
5G is an ideal solution for urban areas because these high frequencies have a very large bandwidth keeping everyone connected. 5G Frequency Bands vs. 4G can now hit the maximum speeds of up to 100 Mbps though its performance in the real world is generally no more than 35 Mbps.
These 5G frequency bands offer speeds as high as 20Gbps. While 4G provided a one-size-fits-all kind of connectivity where every device got the same service 5G is different. How 5G Could Change the World.
LTE 3GPP Rel8 LTE Advanced 3GPP Rel12 Device categories. For better understanding 1 Gigabit is made from 1000 Megabits. This is the fundamental difference between 5G and 4G.
4G speed test reveals that 5G tends to be about 100 times faster than 4G with speeds reaching 10 to 20 gigabits per second Gbps against 100 megabits per second Mbps offered by 4G. 5G is designed to connect many more types of devices than smartphones anything really. However the speed and latency in early FR1 deployments using 5G NR software on 4G hardware non-standalone are only slightly better than new 4G systems estimated at 15 to 50 better.
1Gbps and higher as per need. There are a total of 9 different frequencies used in the UK used by the mobile networks to deliver their 2G 3G 4G and 5G mobile services. Peak Data Rate.
Thats a stark difference from the 100 times-faster-than-4G speeds on high frequency 5G networks. Why is 5G bad. The comparison of 4G frequencies with 5G frequencies.
The Fifth Generation network uses radio frequencies higher than 30 GHz. The radio spectrum is broken up into bands each with unique features as you move up into higher frequencies. Low- and mid-band versions of 5G use some of the same frequency bands as 4G ranging between 600 MHz42 GHz.